1. Introduction
To find the product of two or more numbers is called multiplication. Multiplication is one of the four basic operations and it is also called the repeated addition of numbers.
For example: 2 + 2 + 2 = 6. At the same time we can write 2 × 3 = 6
5 + 5 + 5 + 5 = 5 × 4 = 20
1.1 What are multiplicand, multiplier and product?
When we multiply, the number being multiplied is called a multiplicand and the number of times the number gets multiplied is called a multiplier.
When we multiply two numbers, the result is the product.
Example: If Devanshi is sharing 2 chocolates with each friend and she has 4 friends. How many total chocolates does she have?
Solution:
She has 4 friends.
She is sharing a number of chocolates with each friend = 2
Total number of chocolates = 4 × 2 = 8
Here 4 is the multiplicand, 2 is a multiplier and 8 is the product.
1.2 How to Multiply?
Steps to multiply by a single-digit multiplier:
- Write the larger number on the top.
- Multiply one's place of the bottom number by the one's place of the top number.
- After that, multiply the ones place of the bottom number by the tens place of the top number.
- Similarly multiply with the rest of the places to get the product.
Steps to multiply by double-digit multiplier:
- Write the larger number on the top.
- Multiply one's place of the bottom number by the one's place of the top number.
- After that, multiply the ones place of the bottom number by the tens place of the top number.
- Similarly multiply with the rest of the places.
- Write a zero in the one's column below the first product.
- Now, multiply the tens place of the bottom number by the one place of the top number and similarly multiply with the rest of the places.
- Add one's digits, tens digits, hundreds, and thousands of digits of both numbers.
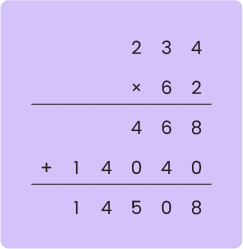
For Example: Multiply 234 and 62.
2. Multiplication:
2.1 Multiplication of a Number by 10, 100 and 1000
- To multiply a given number by 10, put one zero at the right of the given number.
Example: 23 ✖ 10 = 230
- To multiply a given number by 100, put two zeros at the right of the given number.
Example: 78 ✖ 100 = 7800
- To multiply a given number by 1000, put three zeros at the right of the given number.
Example: 9 ✖ 1000 = 9000
2.2 Multiplying positive and negative numbers:
- Multiplication of a positive number with another positive number always gives a positive product. Example: 2 ✖ 7 = 14
- Multiplication of a negative number with a positive number always gives a negative product. Example: -5 ✖ 9 = -45
- Multiplication of a negative number with another negative number always gives a positive number. Example: -7 ✖ -6 = 42
2.3 Multiplying Decimals
Firstly, multiply the numbers as whole numbers, but ignore the decimal point for now. After multiplication, count the number of digits after the decimal in each factor. Finally, put the same number of digits behind the decimal in the product.
Example: Find the product of 0.2 and 0.4.
First, multiply whole numbers i.e. 2 and 4.
Since 2 ✖ 4 = 8
Now, place a decimal in the product.
Since the total number of digits in 0.2 and 0.4 after the decimal = 2,
But 8 has one digit so put 0 before 8 to make a two-digit number and place decimal as shown.
0.2 ✖ 0.4 = 0.08
2.4 Multiplication of fractions
- First multiply the numerators.
- Now, multiply the denominators.
- Reduce the final fraction to its simplest form.
Example:
4⁄6 ✖ 3⁄5 = ![]() = 12⁄30
= 12⁄30
Now reduce the fraction.
Since HCF of 12 and 30 = 6
Hence, 12⁄30 ÷ 6⁄6 = 2⁄5













