GCSE Solved Topic Wise Questions
5320+
Students
70% OFF
£89/year
Add to Basket
- Practice 7K+ topic-wise questions, tagged by difficulty and time.
- Unlock instantly, 2026, GCSE exams, 200+ Maths Past & Predicted Papers.
- Access detailed step-wise solutions by GCSE examiners on the website.
- Get full GCSE Maths exam syllabus & download paper planner.
- Boost exam speed, accuracy, & confidence for GCSE exams.
- Suitable for Edexcel, AQA, OCR, WJEC, CCEA & Eduqas boards.
70% OFF
£89/year
Add to Basket
GCSE Exam Topics
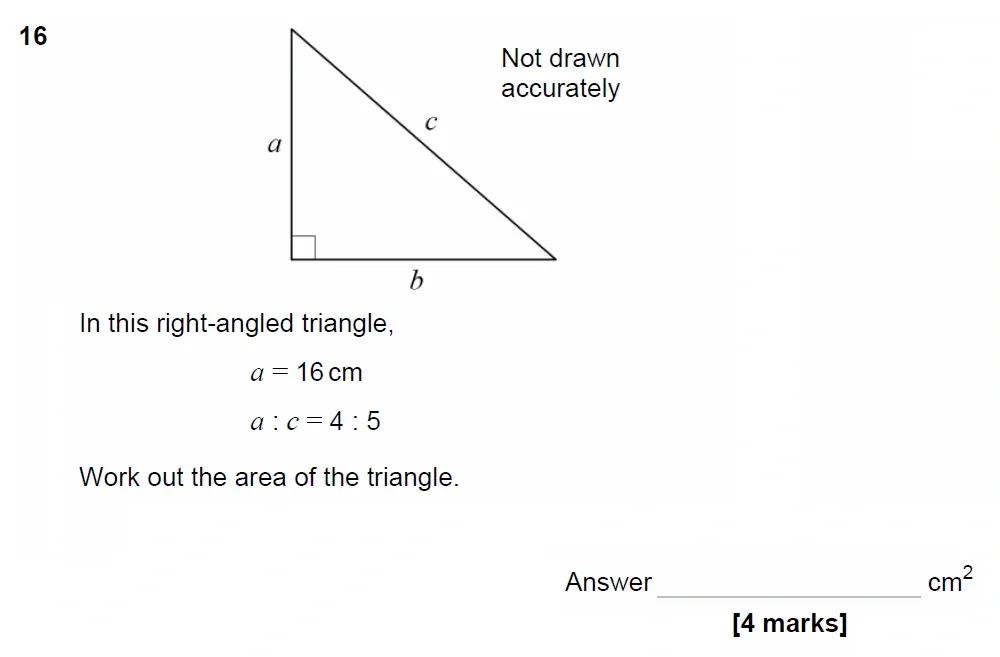
Pythagoras Theorem - GCSE Maths Exam Questions & Answers
Use Calculator :Yes
Use Calculator :Yes
2:00
Topics Covered:
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :No
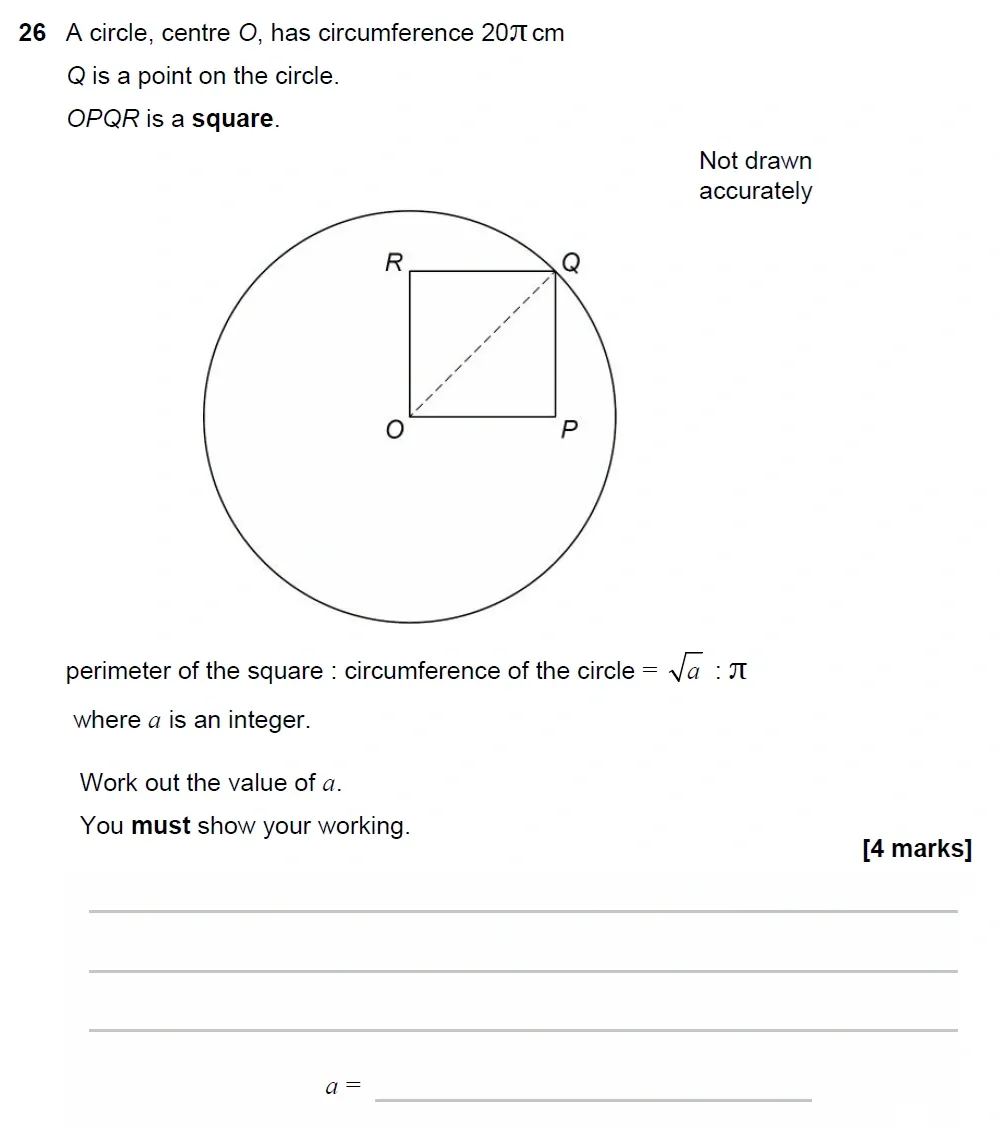
Use Calculator :No
3:00
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :Yes
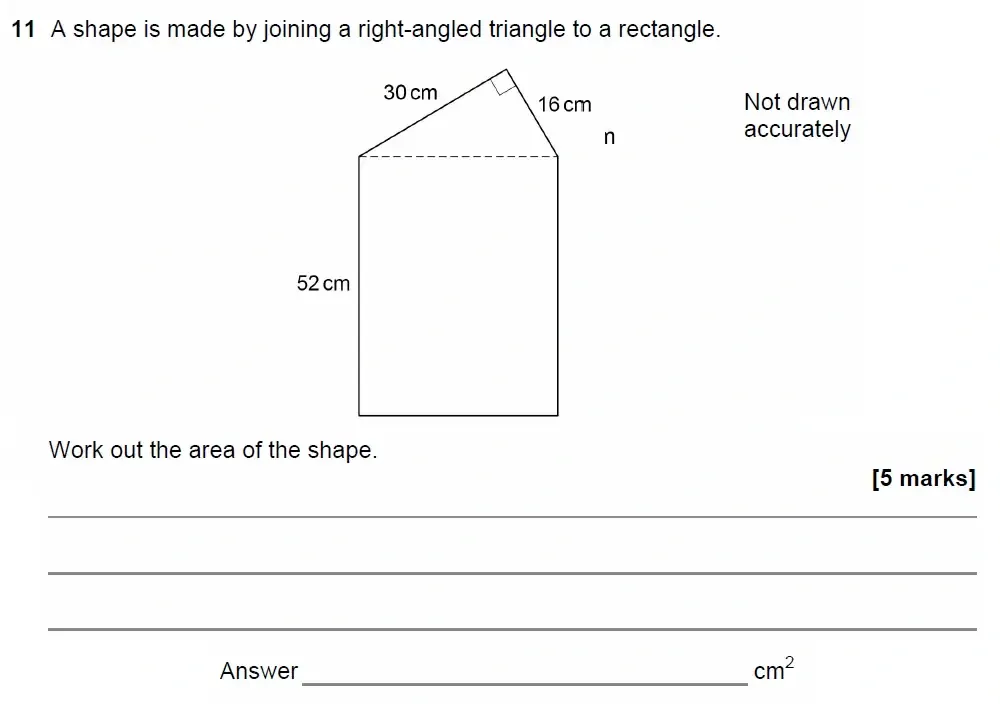
Use Calculator :Yes
3:00
Topics Covered:
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :Yes
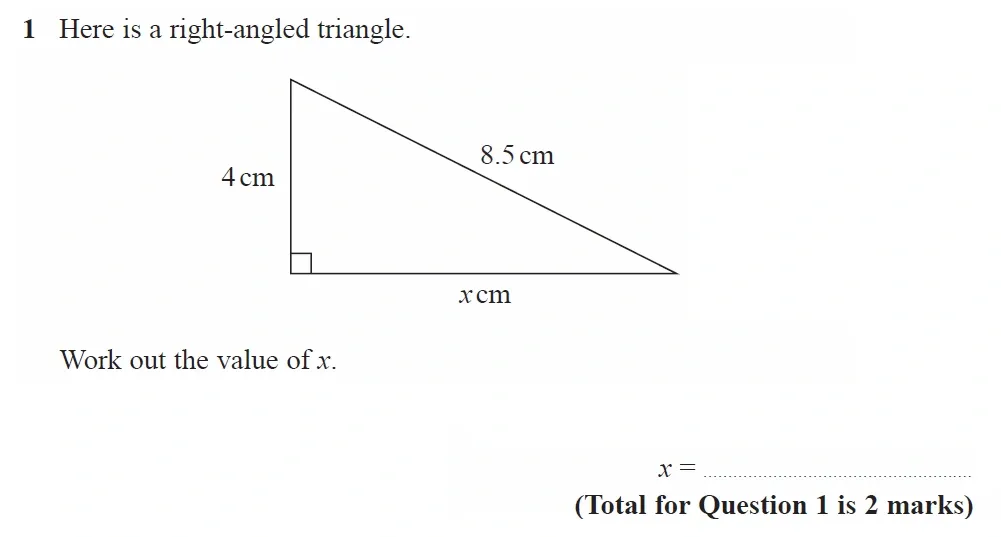
Use Calculator :Yes
1:00
Topics Covered:
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :No
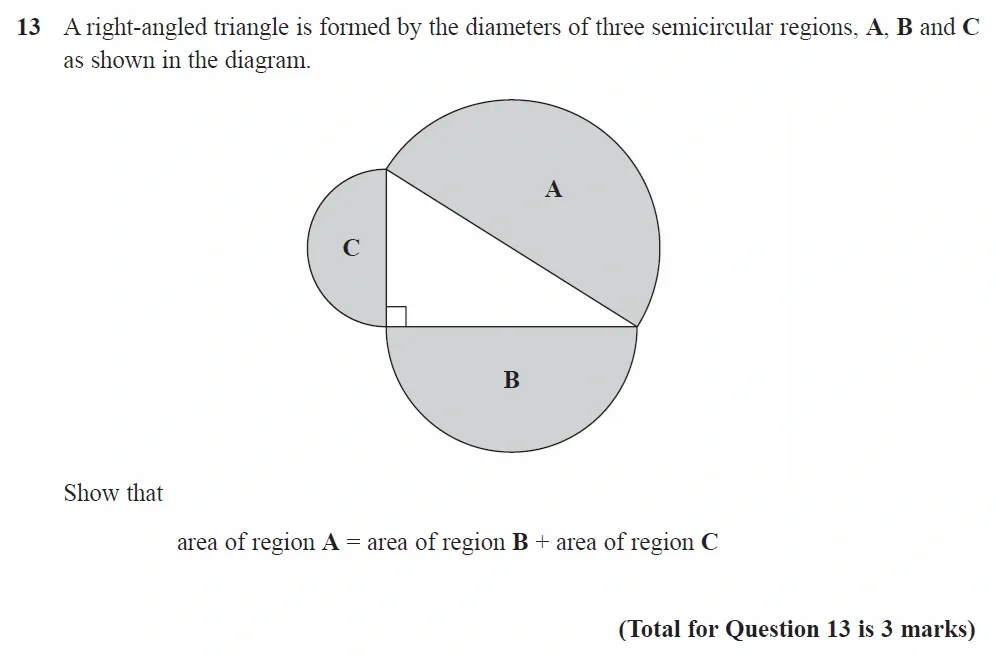
Use Calculator :No
2:00
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :Yes
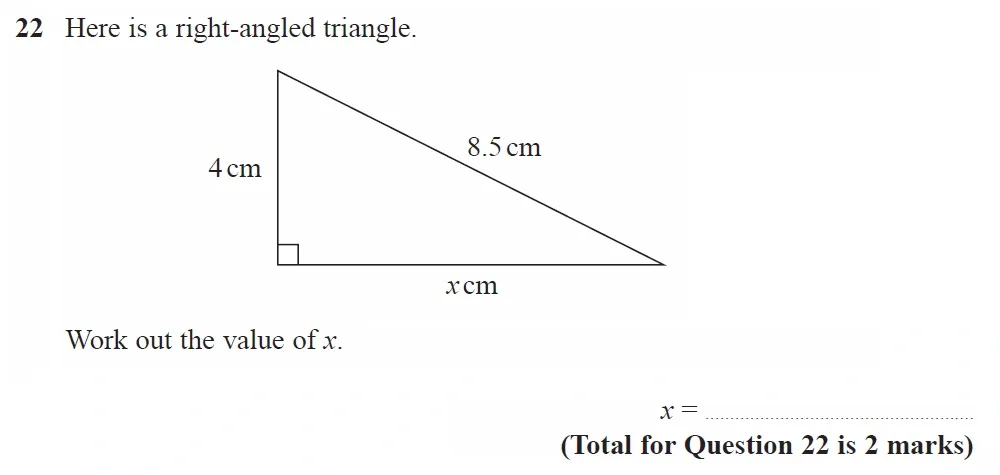
Use Calculator :Yes
2:00
Topics Covered:
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :Yes
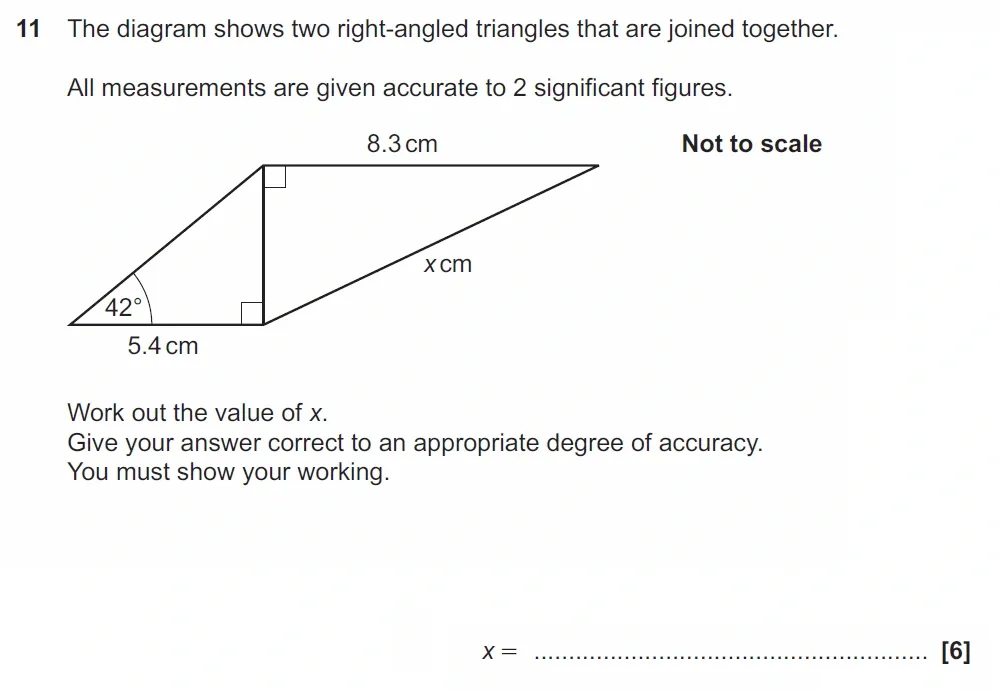
Use Calculator :Yes
3:00
Topics Covered:
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :No
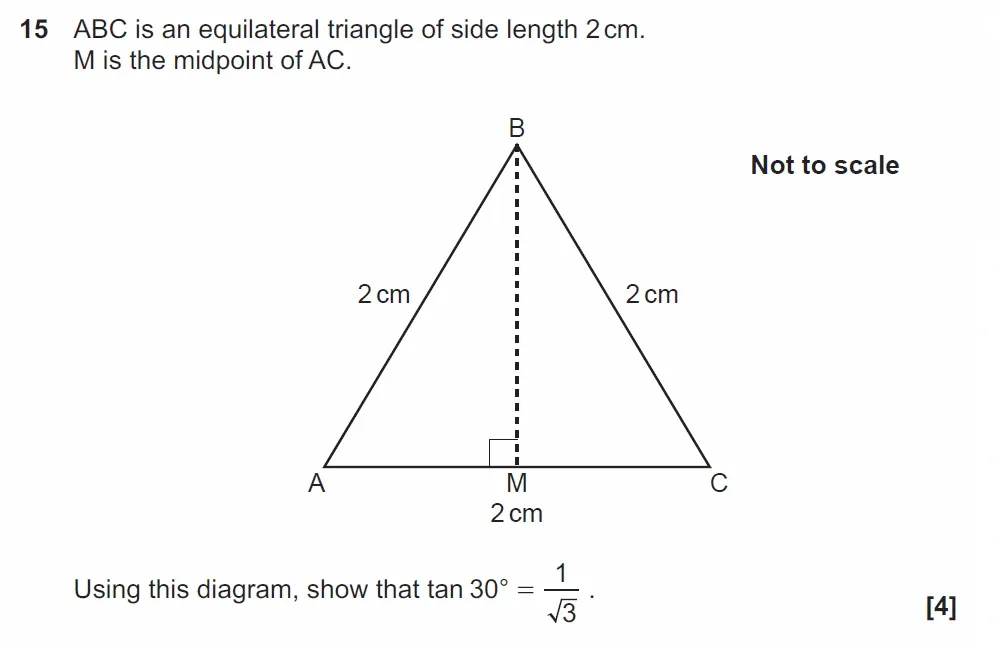
Use Calculator :No
2:00
Topics Covered:
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :Yes
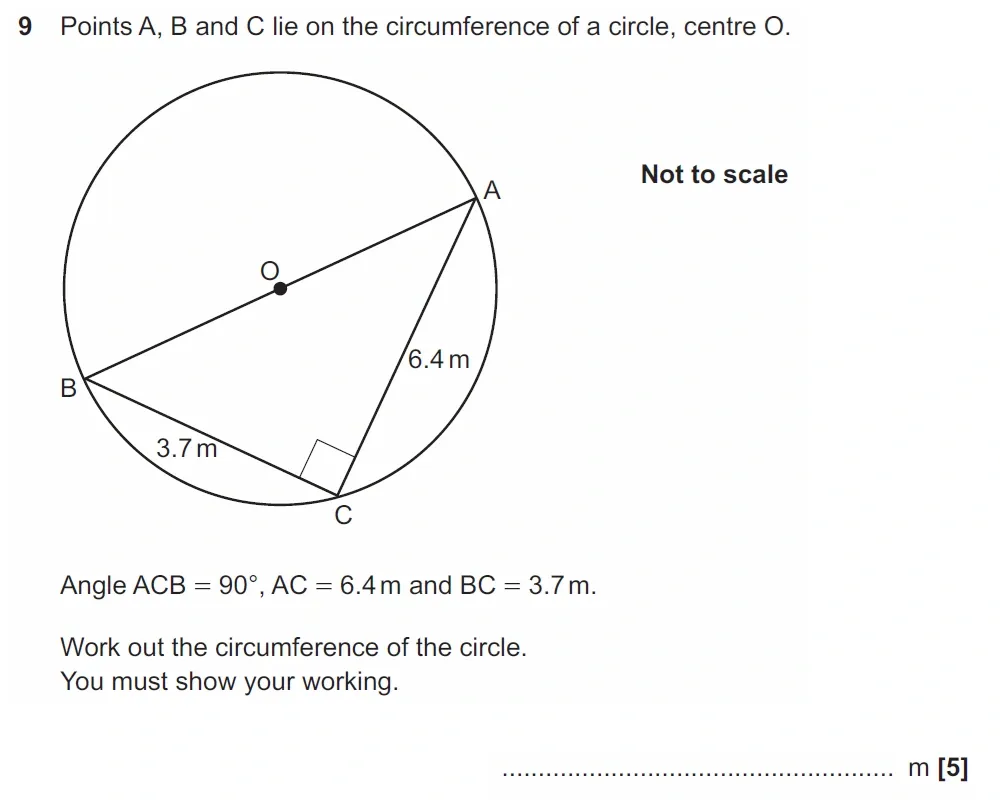
Use Calculator :Yes
2:00
Topics Covered:
Use Calculator :No
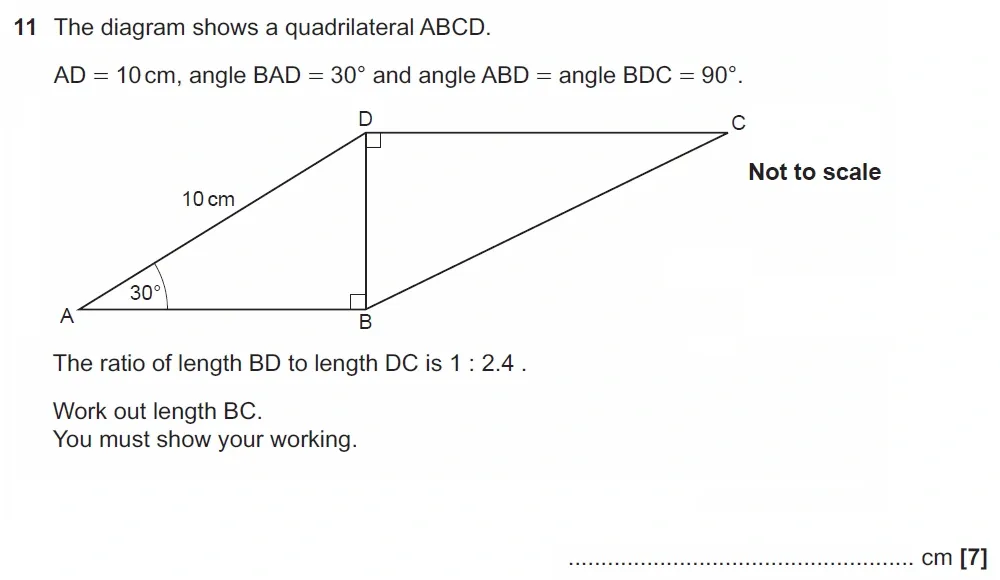
Use Calculator :No
2:30
Topics Covered:
Key Feature of GCSE Solved Topic Wise Questions
Detailed Answers
Step-by-step solutions to GCSE Maths papers designed to build core concepts and boost exam confidence.

Benefits of GCSE Solved Topic Wise Questions
How to Use of GCSE Solved Topic Wise Questions
Step 1

Select your practice topic
- Select GCSE Maths topic of your choice from the left side menu.
- Create a study plan with the downloadable planner.
Step 2

Mark Your Answers

- Solve GCSE Maths past papers questions under timed conditions.
- Mark your answers with the answer explanation provided.
Step 3

Track the progress

- Identify and work on weak GCSE Maths questions.
- Solve 200+ GCSE maths past papers and Answers (Complimentary Access).