
Let’s explore Present Tense examples!
Tenses can often be confusing. Use our guide to aid your understanding of how to use the present tense with ease!
When Do We Use the Present Tense?
In English, we have verb tenses to indicate actions or states of being. The present tense describes an action happening now or a current state of existence.
Examples of actions happening now:
- Saffir is singing in the choir.
- Nahom is running to the bus stop.
- Fleur looks in the mirror to check her make-up.
Examples of describing a current state of existence:
- Dora is happy today.
- Brody seems a little angry right now.
How Many Types of Present Tense are There?
There are four versions of the present tense. These are:
- Simple present
- Present progressive
- Present perfect
- Present perfect progressive

What is the Simple Present Tense?
The simple present tense is used:
- To describe factual information and habits:
- I sing.
- I go running.
- I like cats.
- It is always foggy this time of year.
- Felicity reads a book every day.
(Please note, they do not have to be occurring right now.)

- To describe scheduled events in the future:
- The bus arrives at 10 am.
- The flight is expected to be on time.
- To tell stories or jokes to make your desired audience feel more engaged with the story:
- A grasshopper walks into a restaurant and orders a drink. The waiter says, “You are famous around here – we have got a drink named after you.” And the grasshopper says, “Really? You have got a drink called Nigel?”
- The door of the bus opens, and I suddenly feel all eyes on me!
(This may also be known as the fictional present or the historical present.)
How Do I Form the Simple Present Tense?
- First-person singular = I sing
- Second person singular = You sing
- Third person singular = It/She/He sings
- First-person plural = We sing
- Second person plural = You sing
- Third person plural = They sing
Note: The base word (sing) only changes with the third person singular (he/she/it) by adding either ‘s’, ‘es’, or ‘ies’.

Using the simple present for questions
Use for a closed question:
- Do/Does + subject + verb base form:
- Does Gordon drive?
Use for an open question:
- Interrogative + do/does + subject + verb base form:
- When does Big Ben chime?
Important Spelling Rules to Remember With the Simple Present Tense:
For regular verbs, add ‘s’:
- run = runs
- remove = removes
For verbs that end in ‘s’, ‘ss’, ‘sh’, ‘ch’, ‘x’, and ‘o’, add ‘es’:
- press = presses
- cash = cashes
- mix = mixes
- do = does
For verbs that end in a consonant + ‘y’, change the ‘y’ to ‘i’ and add ‘es’:
- cry = cries
- reply = replies
What is the Present Progressive Tense?
Sometimes also referred to as the present continuous tense, this verb form expresses current actions, those that are in progress, or actions to happen in the very near future.
Feeling a little confused? Have a look at these present progressive tense examples:
- Happening now: I am running.
- Actions that are in progress: I am studying for my exams.

Actions that will happen soon: I am going to see a play at the theatre on Monday.
How Do I Form the Present Progressive Tense?
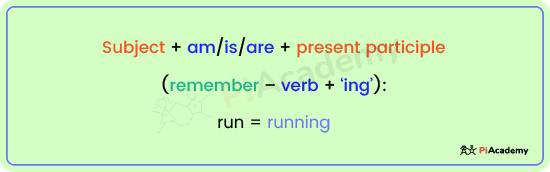
Use this formula:
- Subject + am/is/are + present participle (remember – verb + ‘ing’):
- run = running
More spelling rules!
- When verbs end in ‘e’, remove the ‘e’ and add ‘ing’:
- write = writing
- When verbs end ‘ie’, change the ‘ie’ to ‘y’ and add ‘ing’:
- tie = tying
- For the fun part, when you encounter those verbs whose last syllable is written CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) and is stressed, double the final consonant and add iingi:
- sit = sitting
Want more present progressive tense examples?
Let’s go with the verb ‘To wash’.
- We are washing the car on Sunday.
So, we are simply adding the suffix ‘ing’ to the end of the verb that ends in a consonant without a long vowel sound.
Let’s look at the verb ‘To dig’:
- He is digging a hole.
As you can see, this verb spelling pattern is CVC (consonant – vowel – consonant), which has a short vowel sound, so most of the time we have to add an extra consonant before adding the ‘ing’.
Let’s now look at the verb ‘To captivate’:
- The view of the mountain is captivating.

Here, the verb ends with a silent ‘e’, so we take it away before adding the ‘ing’.
What is the Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense describes an action that originated in the past. Let’s explore some examples:
- She has moved the car to the other side of the car park.
- They have been awake for hours.
The action that is being referred to is often still happening in the present. This is what distinguishes the difference between the present perfect and the simple past tense.
Examples of present perfect vs simple past:
Present perfect
- They have set off late. (We can assume they are still on their journey.)
Simple past
- They set off late. (We can assume they have arrived.)
Present perfect
- Martha has worked at the store for ten years. (This sentence connotes that Martha still works at the store.)
Simple past
- Martha worked at the store for ten years. (We can assume that Martha no longer works at the store.
How do I form the present perfect tense with regular verbs?
Use this rule:
Subject + has/ have + past participle.
- Martha has worked.

Past participle rules!
When you encounter a regular verb, the past participle is the same as the simple past tense:
- work = worked
- pour = poured
If the verb follows a CVC (consonant-vowel-consonant) pattern with a short vowel sound, we double that final consonant and then add ‘ed’:
- stop = stopped
- flip = flipped
However, When the final consonant of the verb is ‘w’, ‘x’, or ‘y’, leave that consonant as it is:
- stew = stewed
- mix = mixed
- enjoy = enjoyed
Furthermore, if a longer verb has a stressed first syllable and it ends with CVC, you just need to add ‘ed’:
- enter = entered
If the verb ends with ‘e’, you only need to add the ‘d’:
- time = timed
- fire = fired
If the verb ends with a consonant and ‘y’, replace the ‘y’ to ‘i’ and then add ‘ed’:
- rely = relied
- fry = fried
How Do I Form the Present Perfect Tense With Irregular Verbs?
With irregular verbs, it is simply a case of learning the appropriate past participle and then noticing patterns.
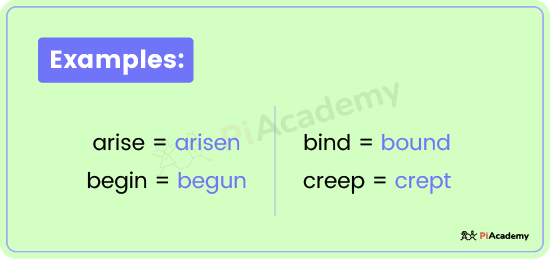
Here are some examples:
- arise = arisen
- begin = begun
- bind = bound
- creep = crept
Other versions of the present perfect
Negative present perfect
To form the negative version of present perfect, use:
Subject + has not/ have not + past participle:
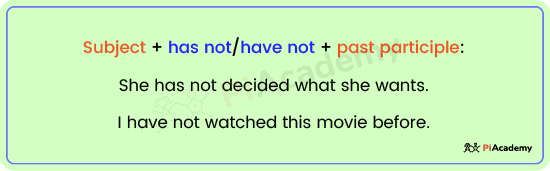
- She has not decided what she wants.
- I have not watched this movie before.
The question version of the present perfect
To form the question version of the present perfect, use:
- Has/ have + subject + past participle (for a closed question):
- Has she decided what she wants?
- Have I watched this movie before?
- [question word] + has/have + subject + past participle (for an open question):
- Why has she made that particular decision?
- Why have I not watched this movie before?
What is the Present Perfect Progressive Tense?
There are two uses for the present perfect progressive tense:
- Action that has begun and is continuing into the present:
- Those flowers have been blooming for weeks.
- Action that began in the past and has finished recently:
- David has been gritting the roads all night.

This is classed as present tense because David has carried out an action that has relevance to the present (the roads are free of frost and ice for the morning commute).
Want another example of the present progressive tense?
Here is another example of the present progressive tense:
- Helen has been waiting for the package to be delivered all day.
(She might still be waiting, or she might have received the package. What we do know, however, is that the waiting has an impact on her current situation.)
How Do I Form the Present Progressive Tense?
Use this rule:
Subject + has been/have been + present participle:
- I have been working on this essay since last week.

Other versions of the present progressive tense:
Negative Present Progressive
Subject + has not been/have not been + present participle:
- I have not been able to sleep properly for a while.
Question version of the present progressive tense
To form the question version of the Present Progressive, use:
- Has/ have + subject + been + present participle (for a closed question):
- Has Dominic replied to the invitation?
Question word + has/have + subject + been + present participle (for an open question):
- Why has Dominic not replied to the invitation?
Sneak Peek of Pi Academy Resources
Now that we have explored the present tense, why not try out our practice papers and exercises on our website!